In the practice of Design Thinking, prototyping is an integral part of the design thinking and user-centered experience within a project. In particular, it allows us to test our ideas quickly in order to confront them with the reality on the ground.
Cardboard prototype of an agency toaster Quirky
# WHAT IS A PROTOTYPE?
A prototype is a physical or digital object resulting from an idea that is represented in whole or in part. In a design project, it is a question of illustrating our hypotheses concerning a service or a tool, imagined during the ideation phase. Be careful though, a prototype is not a finished product.
When you start a project from scratch, you often don't have a lot of resources or time. This is why our ideas must be tested, modified, improved, by integrating the constraints of production speed.
As our daily habits can change, we are obliged to confront our ideas to our users, so that our final solution meets the expectations and needs of our users.
Example of a test session of a “low fidelity” prototype ofUX Playground
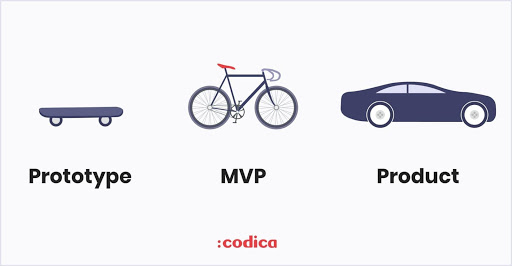
# WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN A PROTOTYPE AND AN MVP?
Prototyping and MVPs are two close deliverables, that complement each other in a project.
Illustration taken from the article Medium of Codica “Is an MVP the Same as a Prototype?”
A prototype is never commercialized or industrialized. It is there to be presented and manipulated by our referring users in order to generate feedback on our hypotheses.
If the prototype does not meet expectations testers, so we go out with new elements to be taken into account for the project and for our future iterations. We save time and money because we make sure not to go down the wrong path.
But if our hypotheses are validated, the realization of a marketable version on the basis of these validated returns can be envisaged.
That's when the MVP kicks in, it's the simplest, rawest, marketable version of the product.
# WHY PROTOTYPE IS NEEDED?
To refute or confirm your assumptions that emerged during your ideation phase. Normally you will have more or less formalized ideas of what to do.
The prototype will allow you to put your ideas into physical form and make your concepts interactive to get user feedback quickly.
It's a perfect way to speak the same language and facilitate discussions not only with your users, but also with the teams in charge of the future design of the product, especially if you find that your team has a different business language than yours
Example : PO, developer, business referent, engineer, salesperson, etc.
The prototype can also inspire project stakeholders in a broader way.
Paper prototyping is a great alignment tool between each team person
To save time, cost and energy, rapid prototyping should formalize only part of your assumptions, whether digital or physical, and not the entire project.
If you prototype too many hypotheses at the same time, the risk is that you no longer know which hypothesis best suits your users, and can even complicate your basic solution.
When you imagine a new product, I think you want its success, however it is important at the beginning of the project to know how to start small. Learn during the ideation phase and confront your ideas with users all the time to grow your solution.
# HOW DOES A PROTOTYPE WORK?
If we have to summarize only in three points, rapid prototyping allows us:
- To have tangible elements to carry out tests.
- Formulate a value proposition through clear messages
Example : Your target, the function highlighted, the service you offer, its major advantage, the benefit.
- To create visibility in a project.
So encourage your project team to target a portion of users or a niche market instead.
From a financial point of view, prototyping allows not to cost too much in the budgets of a project, especially for the team of developers.
It generally has a low investment cost, because it is not the finished product and the aim is only to provide qualitative information.
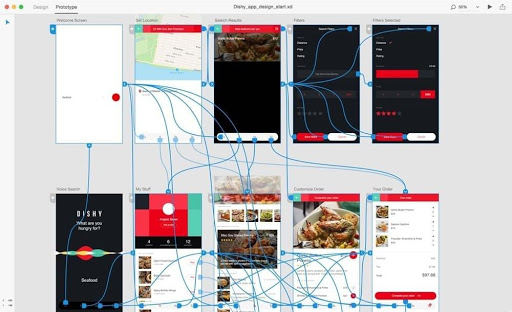
Example of a high-fidelity model prototyped in Adobe XD and ready to be tested
When you have your first prototype tested, there is a good chance that the results will not be what you expected, so do not be disappointed and capitalize on it.
We rarely find the right solution the first time, you have to see your prototype more as an opportunity to design a product that meets the real needs of your end users.
It happens that some prototypes need a high level of fidelity, this is the case of chatbots which are not necessarily easy to prototype and to make tangible.
However, prototyping a sculpin will allow you to carry out tests on your priority target who will use your future tool.
With current tools, you can create a prototype that will look like your chatbot without having to code a single line, ideal for limiting budget and human resource costs. You can also offer several versions of a prototype to test the interface, the conversation flows, the user journey on the tool.
In the world of prototyping, there is not only screen prototyping but also hardware prototyping using paper, cardboard and of course the Arduino.
Example of an Arduino prototype coupled with a smartphone
Arduino is an open source electronic platform for electronic prototyping. An Arduino board can connect to other objects like sensors, helpers, buttons, screens, etc.
The Arduino is particularly popular for prototyping connected objects: one of the best-known examples using Arudion technology is being able to control a light bulb with a phone app.
Be careful though, to create interactions with an Arduino, you unfortunately need to know how to program a little, but there are many sites that can help you get started.
# EIGHT TOOLS TO MAKE YOUR PROTOTYPES
Choosing the right tool will best illustrate your thoughts and to improve the work with your customers. Now many prototyping tools exist, I suggest 5 tools that will allow you to formalize prototypes for your new projects.
- Cards, paper and pencils : The tool that will be most often used in our trade! The prototype will often be reformulated later in detail on the machine in order to make it understandable to everyone. The advantage of this tool is that you can cut it, paste it, scan it to perform the first tests for your users.
- Adobe XD : For the moment free, you can create interactive prototypes and even production-ready assets in a single application. If your collaborators are remote, you can share a link for them to comment on.
- Origami Studio : We can preview the model live on your mobile in real time like on Adobe XD using Origami Live. But you can also export your components and their animations so that developers can integrate them into the project.
- wireframe.cc : To make “low fidelity” prototypes, the handling is quick for a clean result. the annotation system is very practical for commenting on your work.
- Hype 4.0 : To produce animations as in After Effects for high quality oriented prototypes, the principle is to create animations via key points. The advantage of this tool is that it is not necessary to know the code.
- BotMock : No need to know how to code to use it, you can make chatbot prototypes ready to be developed. The software offers enough possibilities. In particular, it can map conversation flows and view them from a user's perspective.
- Framer : If you use Arduino to design and prototype an electronic system, you can use Framer X to design and prototype its interface. This software is recommended for making functional interfaces.
- My Workshop In Town : If you have the soul of a handyman, there are many fablabs in Paris, which have various equipment such as 3D printers and laser cutters, ideal for working on the hardware of a prototype.
# REFERENCES
- How about making a paper prototype? : Article of Christophe Pian on the Medium site.
- Is an MVP the Same as a Prototype? : Article of Codica on the Medium site.
- UI-UX: the basics of web and app prototyping – Designing for and with users
“It is by making mistakes that we learn and grow. You have to be bad to become good.”
Paula Scher
Enguerran Chambaraud, UX Designer @UX-Republic
UX/UI ECO-DESIGN # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
DESIGN THINKING: CREATING INNOVATION # Belgium
UX-REPUBLIC Belgium
12 avenue de Broqueville - 1150 Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
MANAGING AND MEASURING UX # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
DESIGN SPRINT: INITIATION & FACILITATION # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
UX-DESIGN: THE FUNDAMENTALS # Belgium
UX-REPUBLIC Belgium
12 avenue de Broqueville - 1150 Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
GOOGLE ANALYTICS 4 #Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
ACCESSIBLE UX/UI DESIGN # Belgium
UX-REPUBLIC Belgium
12 avenue de Broqueville - 1150 Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
EXPERIENCE MAPPING # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine