By integrating a discovery or project framing phase, we are often confronted in B2E projects with complex environments in which it is sometimes difficult to clearly perceive what the problem to be addressed is; what are the necessary data that will allow us to frame our objectives, our assumptions and the keys to success.
It is to this extent that the Ergonomic Work Analysis (AET) becomes interesting. It allows us, as UX Designer to approach a systemic vision; to be able to study the whole of work situations: the people, the tasks they have to perform, the way they have to go about it, the environment in which they find themselves, the equipment and the tools they use, the instructions they receive...
What is the impact/objective of ergonomic work analysis?
The impacts/objectives :
- Situate the risks globally and avoid their movements
- Propose and/or improve the MVP ; minimum viable product/service
- Improve working conditions employees/users
- Improve production quality and efficiency
- Protect health people.
To learn more ⇒ What is the purpose of the analysis of the activity in Ergonomics? Francois Hubault
What is the role of a UX Designer in the AET?
At the heart of this process, we are led to design impactful scenarios, of a service and/or a product serving at the same time, to meet the specific needs of users, but also of their environment.
Going so far as to borrow the role of an ethnographer and of cognitive sciences, this methodology places and/or replaces the UX/UI designer in the posture of empathy. It makes it possible to put people and their environment at the center of reflection and action in order to design tomorrow's services and customer experiences differently.
The UX designer can, in this case, use this method from the discovery phase of the project. Its role is precisely to:
- Observer and to analyze work situations in the real context of use of the product/service.
- Collect as much data as possible on the behaviors, desires and interactions of the user, via the Shadowing method for example.
- To bring the best possible match between the physical and mental particularities of the workers/users
- Reply production goals
How?
Ergonomic work analysis makes it possible to understand and question work activity, based on ergonomic observations and direct in situ surveys.
Understand et observer the users in their environment internal allows to go to the heart of the knowledge of the field and user empathy. This mainly allows identify the gap between prescribed work (the tasks provided to employees by the company), and the actual work (operating compromises, hazards and variations in the situations that employees/users are confronted with in their activities).
To use the concept of A Winner (1994), “activity analysis” ergonomics, integrates a phase of collaborative or even collective learning making it possible to capture the experience of users, their activities and the real uses of the work. To do this, it is useful to know promote the expression of employees (EX) on their work activity in a spontaneous way:
- What actually happens in the work activity?
- Why is the work done this way?
- What are the effects of work on the individual, on groups and on the structure?
- Does the way in which the work is carried out really contribute to the performance of the company and how?
- Etc
source: https://www.anact.fr/file/9931/download?token=z6jIPi9d
The main stages of the tests B2E applications
In order to question these activities, it is useful to list, map and finally select the relevant information. To do this, ergonomic work analysis involves three main phases of user research a interview phase and an analysis phase and a conception phase.
Interview stage
1. Build a custom test protocol
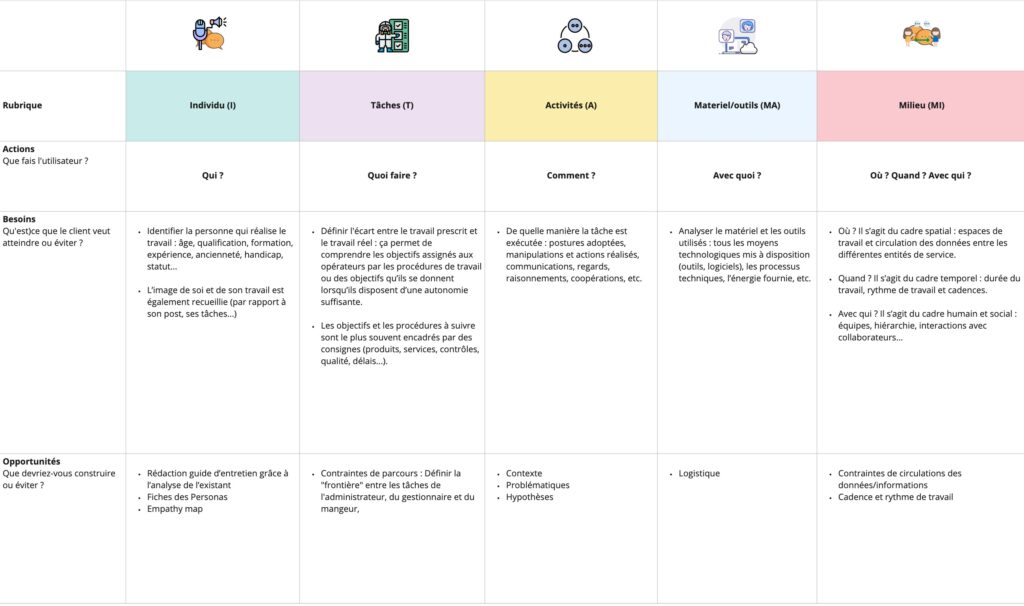
To capture the gap between prescribed work and actual work, and methodically describe the information collected during the observation phase, the ITAMaMi method, initially created by the CARSAT (Retirement and occupational health insurance fund) to analyze accidents at work, makes it possible to classify and analyze the different paths of the employee, according to 5 headings:
source: Nour Hebiri, Cartography of the ITAMaMi method, 2022
As explained in the map above, headings make it easier to take notes. The UX Designer can use this template to note the risk factors and associated constraints. The results grid can also be implemented by adding items on the needs and objectives of the client (of the company).
2. Observe, interview, listen to and record testers
- It is recommended to put yourself in optimal conditions so as not to distort the test during the interviews.
- To assess the mental load, do not hesitate to question the employee (according to his age, qualification, training, experience, seniority, disability, status, etc.). In situ, the mental evaluation makes it possible to identify what really contributes to lightening or increasing one's daily workload (arch which is often higher than the prescribed work). This assessment allows employees to be more fulfilled and productive, and to increase the company's performance not only in terms of its attractiveness but also in terms of its ability to innovate.
It is equally important to specify that depending on the availability of users, the observation and interview phase takes about 2 weeks of research.
Tips
When observation phase, we can for example use the method of shadowing. This method will allow us to observe the experience of employees/collaborators (EX) in their real environment. This includes feelings and experiences at each point of contact: how he handles the tools, with whom he collaborates, are the digital tools used and the interfaces adapted to the user and his activity...
Analysis phase
After noting, describing and categorizing the elements that make up the work situation, the next stage of the analysis consists of analyzing and interpreting these test results to prioritize the problems to be addressed and validate our hypotheses.
We can therefore analyze the Brand Experience (BX), that is to say the elements of the customer experience and the employee experience by noting with the help of post-it notes:
Employee experience (EX): display positive and/or negative effects Customer experience (CE): display positive and/or negative effects
source: Nour Hebiri, Brand Experience Analysis around a Focus Group workshop, 2022
This template is collaborative. You can also show it to collaborators or organize a focus group workshop so that they can add their comments in these cells (note the irritants and discuss them later via commented courses) This can only be enriching 😉
Conception phase
The UX Designer finds its source in a founding discontinuity: that which obliges to make the distinction between:
Task : appropriation of tools,
The behaviour : ownership of procedures
Activities : appropriation of work gestures, teamwork how they collaborate with each other….
The interface functionalities must be able to guarantee the adaptability of the final solution to the needs and expectations of the employees and the company. It is also recommended to hold meetings to brief the development teams. The rapid prototyping of the courses provides a good working basis for testing and validating the essential functionalities of the interface and its ergonomics.
Tips
The ergonomic analysis of the work makes it possible to facilitate the design stages: the architecture of the information, the users flow, the content of the fields and all the functional and technical elements in the design phase.
The objective, let's not forget, is to facilitate and improve the use of solutions and/or digital means made available to employees and collaborators in order to converge towards quality experiences, sometimes lived in as a user (UX, user experience), sometimes as a customer (CX, customer experience) and sometimes as an employee/collaborator (EX).
Last word
Ergonomic work analysis is very effective in optimizing B2E applications, especially if we keep in mind that around 67% of employees are not motivated at work. In reality, what is expected is to optimize human-machine interaction (HMI), by replacing the human at the center of its strategy, which amounts to:
- Improve their engagement and therefore their productivity
- Facilitate and enhance the management of tasks in order to optimize their journey and therefore their time
- Present a scalable business solution that can be adapted to digital tools and future IT applications
Nour HEBIRI, UX Designer @UX-Republic
Our next trainings
UX-DESIGN: THE FUNDAMENTALS # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
VISUAL THINKING: CONCRETE YOUR IDEAS # Paris
UX-REPUBLIC Paris
11 rue de Rome - 75008 Paris
DIGITAL ACCESSIBILITY AWARENESS #Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
DIGITAL ACCESSIBILITY AWARENESS #Belgium
UX-REPUBLIC Belgium
12 avenue de Broqueville - 1150 Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
ACCESSIBLE UX/UI DESIGN # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
AWARENESS OF DIGITAL ECO-DESIGN # Belgium
UX-REPUBLIC Belgium
12 avenue de Broqueville - 1150 Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
STORYTELLING: THE ART OF CONVINCING # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
UX/UI ECO-DESIGN # Paris
SMILE Paris
163 quay of Doctor Dervaux 92600 Asnières-sur-Seine
DESIGN THINKING: CREATING INNOVATION # Belgium
UX-REPUBLIC Belgium
12 avenue de Broqueville - 1150 Woluwe-Saint-Pierre